Abstract
NLP에서는 Transformer 구조가 사실상의 표준으로 자리잡았으나, CV에서는 응용이 제한적
- CNN에 결합해 사용하거나, CNN의 기본 골격을 유지한 채 일부분을 transformer로 대체하는 역할 정도에 그침
본 논문은 이러한 CNN에 대한 의존이 필수적이지 않으며, image patch에 직접 pure transformer를 적용해도 classification 문제에 좋은 성능을 보임을 확인
Vision Transformer(ViT)는 적은 계산량에도 불구하고 여러 벤치마크에서 state-of-the-art CNN에 비교해서도 좋은 성능을 보임
Introduction
Transformer를 위시한 self-attention 기반 아키텍처는 NLP의 주류로 사용되고 있음, 일반적으로 거대 corpus로 훈련 후 fine tuing하는 방식으로 사용
- Transformer의 계산효율성과 scalability덕분에 전례없던 크기의 (100B 이상) 파라미터 수를 가진 모델들도 훈련이 가능해짐. model과 dataset이 점점 커짐에도 성능이 saturate될 기미를 보이지 않음
그러나 CV에서는 아직 CNN 기반 아키텍처가 주류. self-attention을 결합하려는 시도는 있었으나 ResNet-like architecture들이 여전히 SOTA의 자리를 차지
본 연구에서는 NLP에 영감을 받아 image에 최소한의 수정을 가한 standard Transformer를 적용해 실험.
- 이미지를 패치로 쪼갬 → linear embedding의 sequence → Transformer의 입력으로 사용.
- Image patch가 NLP의 token과 같이 다뤄짐. 지도학습으로 훈련
ImageNet과 같은 mid-size dataset을 strong regularization없이 훈련시켰을 때에는 비슷한 크기의 ResNet보다 수 퍼센트 낮은 성능.
- Transformer는 CNN에 내재된 “inductive bias”가 없음. (translation equivariance, locality, …) → 충분한 데이터가 없으면 쉽게 generalize되지 않음
그러나 큰 데이터셋으로 (14M - 300M images) 훈련시 이를 극복 가능.
- sufficient scale로 pre-training 후 transfer시키면 좋은 성능
- 이미지 인식 벤치마크들에서 SOTA 이상의 성능
Transformer는 NLP에서 매우 널리 사용, large corpora에서 pre-train 후 fine-tune하여 사용하는 경우 많음.
- BERT : denoising self-supervised pretraining task
- GPT: language model을 pretraining task로
Self-attention을 naive하게 적용시 pixel 수의 제곱에 비례 → 비현실적
- Transformer을 image processing 과정의 중간에서 적용하려는 많은 시도들
- e.g. Parmar et al. (2018): 각 query pixel의 근방에 있는 픽셀들에 대해서만 self-attention을 적용 (local multi-head dot product self-attention block) → convolution을 완전히 대체 가능
- 좋은 성능을 보였으나, HW 가속기상에서 효율적으로 구현하려면 복잡한 engineering 요구
본 연구와 가장 연관성 높은 모델: Cordonnier et al. (2020)
- input image에서 2x2 patch를 추출하여 full self-attention을 적용
- ViT와 매우 유사하지만 본 연구에서는 여기에 더해 large scale pre-training으로써 vanilla transformer가 SOTA CNN 이상으로 경쟁력있어진다는 점을 보여주려 함.
- Cordonnier et al. (2020)은 2x2 patch 때문에 small resolution에만 적용가능했다는 한계 극복.
본 논문과 깊은 연관을 가진 또 다른 예시: image GPT(iGPT). image resolution과 color space를 축소한 후, Transformer를 image pixel에 적용.
- 비지도학습, generative model로써 훈련 후 fine tuning / probe linearly
기본 ImageNet보다 dataset size가 커지면(ImageNet-21k, JFT-300M) CNN의 성능이 얼마나 더 좋아지는지에 대해서는 이미 연구가 많이 진행 → 이러한 데이터셋을 이러한 연구들에서 사용된 ResNet 기반 모델 대신 Transformer에 적용
Method
최대한 original Transformer에 가깝도록 설계됨
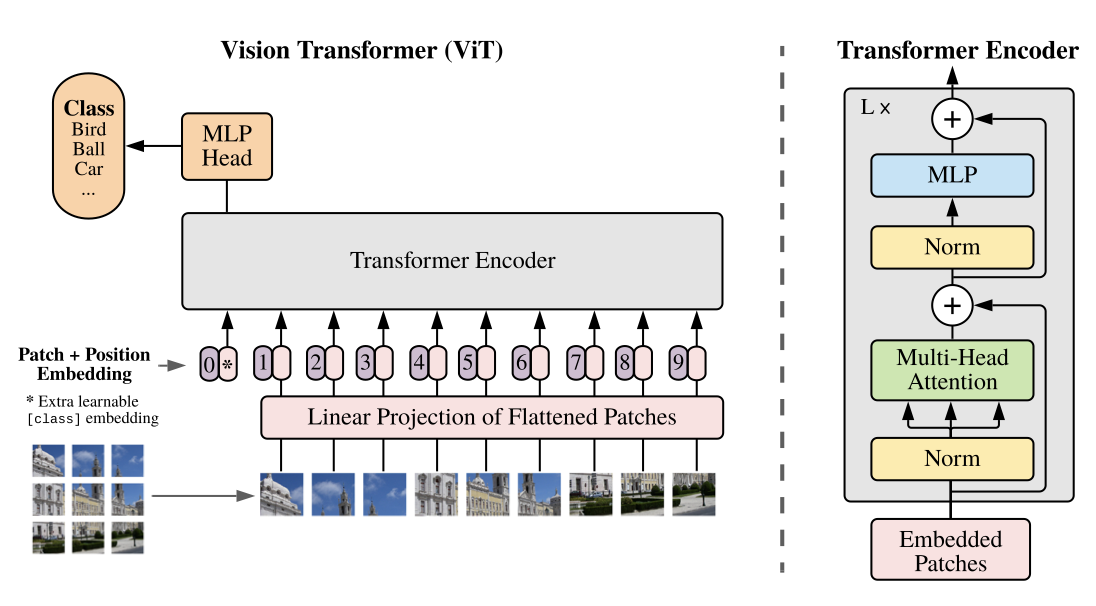
Vision Transformer (ViT)
2D image의 처리를 위해서,
- $\mathbb{R}^{H\times W\times C}$ 모양의 이미지를 $\mathbf{x}_p \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times (P^2 \cdot C)}$로 reshape ($P\times P$: patch의 resolution, $N=HW/P^2$: patch의 개수)
- 모든 layer에서 latent vector size는 $D$로 같음
- 이를 위해서 input에서는 patch를 flatten → traininable linear projection을 통해 D차원으로 바꿔줌 (patch embedding)
- patch embedding에 1D positional embedding을 더해줌
- 2D-aware positional embedding이 더 큰 효과가 있지는 않음
- Transformer Encoder는 Attention is All You Need에서와 똑같은 형태. MLP에는 GELU(Gaussian Error Linear Unit) non-linearity가 적용
Inductive Bias
- ViT는 CNN보다 image-specific inductive bias가 훨씬 약함 (locality, translation equivariance). ViT에서 local, translationally equivariant한 구조는 MLP layer밖에 없음. self-attention은 global
- locality: 2D상에서 인접해 있는 구조
- positional embedding도 2D에 대한 정보를 담지 않으므로 patch간의 spatial relation에 대한 정보는 0에서부터 배우게됨
Hybrid Architecture
- raw input patch 대신에, CNN의 feature map을 image sequence로 넣는 방법도 있음
Fine-Tuning and Higher Resolution
일반적으로 ViT를 large dataset에서 훈련 후 smaller downstream task에 적용
- 이를 위해서는 pre-trained prediction head를 제거한 후 zero-initialized $D\times K$ FF layer를 추가 (K: downstream class의 개수)
더 높은 해상도의 이미지에 적용하고 싶을 때는 patch size를 유지, sequence length가 늘어나도록 함. (임의의 sequence length에 대해 적용 가능)
- positional embedding의 (원본 이미지상의 위치에 따른)2D interpolation을 사용
- 이는 image에 대한 inductive bias가 ViT에 인위적으로 주입된 유일한 측면임
Experiments
ResNet, ViT, hybrid의 representation learning 능력을 평가.
Setup
Dataset
- Pretraining: ImageNet (1k classes, 1.3M images), ImageNet-21k (21k classes, 14M images), JFT (18k classes, 303M high-resolution images)
- 이후 여러 benchmark들로 transfer
- Natural(pets, CIFAR) / Specialized(medical, satelite) / Structured(localization과 같은 geometric understanding이 필요한 작업들)
Model Variant
- BERT에서 사용된 configuration에 기반해 설정. B / L / H
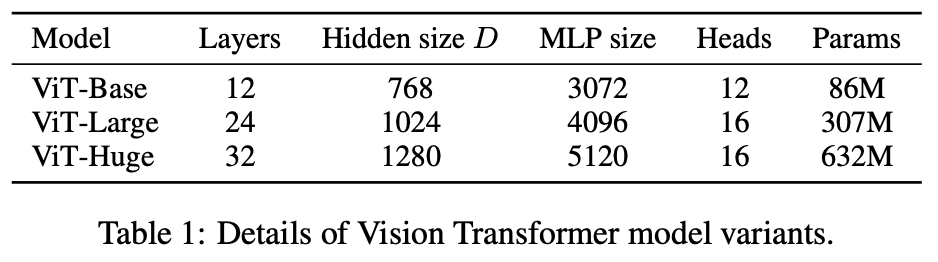
- Baseline CNN으로는 ResNet을 사용하되, BatchNorm을 GroupNorm으로 대체, standardized convolution을 사용
- transfer 성능을 높임 → ResNet (BiT)로 부름 (Big Transfer)
- BiT: Big Transfer
- Hybrid model의 경우 intermediate feature map을 patch size 1(pixel)로 ViT에 넣어줌.
Training & Fine-tuning
- Adam, batch size = 4096, weight decay = 0.1, linear lr warmup & decay
- Fine tuning시: SGD with momentum, batch size = 512,
Metrics
- downstream dataset에 대한 결과를 few-show과 fine-tuning accuracy로 보고.
- few-shot accuracy: train image의 부분집합으로부터 얻은 feature map으로 regularized least-square regression을 통해 얻음
Comparison to State of the Art
비교 대상
- large ResNet에 supervised transfer learning을 하는 BiT → ImageNet 제외 SOTA
- Noisy Student: ImageNet과 JFT-300M에 label을 지워서 EfficientNet을 semi-supervised로 훈련 → ImageNet의 SOTA
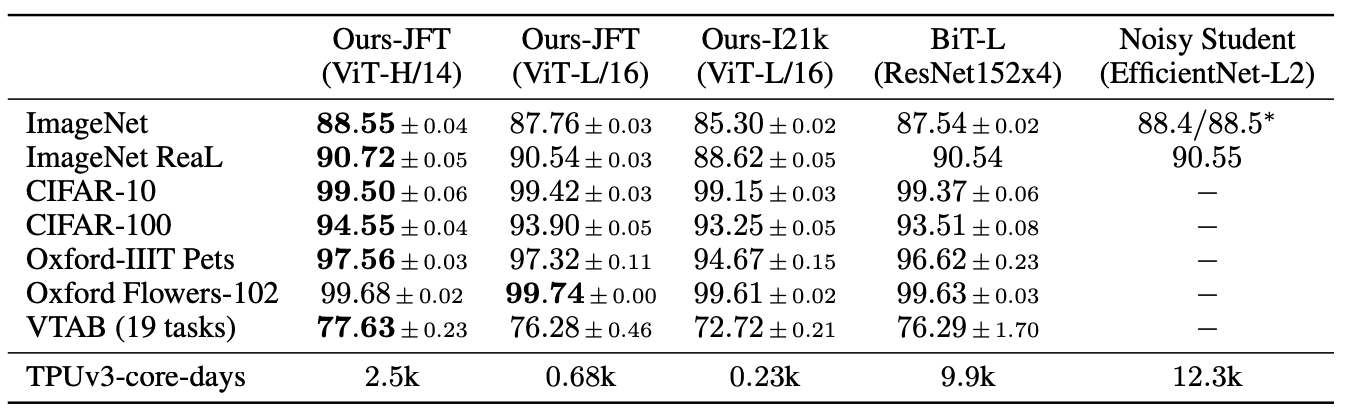
ViT-L/16 model을 JFT-300M dataset으로 사전학습시킨 것이 모든 태스크에서 BiT-L을 이기면서도 computing 자원은 덜 차지
- 더 큰 모델인 ViT-H/14는 (특히 더 어려운 dataset에서) 더 높은 성능
Pre-training Data Requirements
- 데이터셋 크기에 따른 성능 비교. ResNet이 가진 inductive bias 없이 훈련시켰다는 특성이 있으므로 dataset size가 어느 정도로 중요한지를 따져봄
앞에서 매우 큰 사이즈의 JFT-300M dataset으로 pretraining 시켰을 때는 좋은 성능을 보이는 것을 확인.
- ImageNet < ImageNet-21k < JFT- 300M
- 각각을 통해 pre-training 시킨 후 ImageNet으로 fine-tuning. 각각에 대해서 regularization(weight decay, dropout, label smoothing)을 최적화
- ImageNet에서는 ViT-B > ViT-L. ImageNet-21k에서는 비슷한 성능. JFT-300M에서는 ViT-B < ViT-L. 즉, 큰 모델의 장점은 dataset도 커야 살릴 수 있음
JFT-300M의 부분집합 (9M, 30M, 90M)으로 pretranining
- regularization을 최적화하지 않고 같은 hyperparameter 유지
- early stopping으로 best val accuracy를 저장 → few-shot linear accuracy 측정
- 작은 dataset에서는 ResNet과 비슷한 계산자원을 먹을 때 ResNet보다 overfitting이 심함. 반면 큰 dataset에서는 높은 성능
- 즉, 작은 데이터셋에서는 CNN의 inductive bias가 유용하게 사용되지만 데이터셋 크기만 커지면 data로부터 이러한 pattern을 직접 학습하는 ViT의 방식도 충분함
Scaling Study
- model size에 따른 transfer performance의 비교. JFT-300M에서 훈련
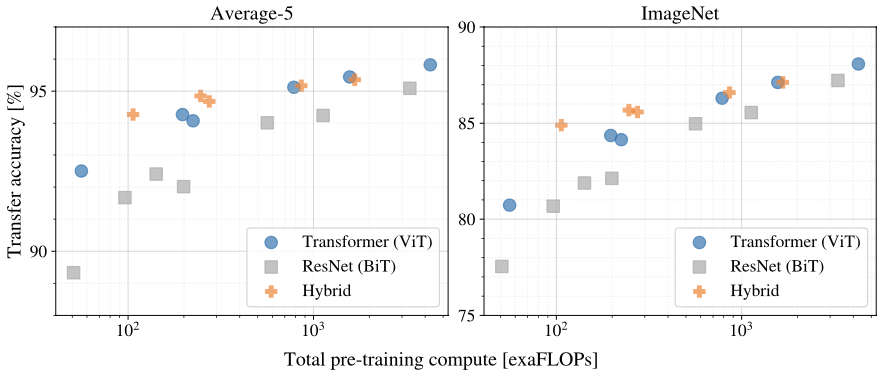
- performance / training time trade-off에서, ViT가 ResNet보다 우위
-
computation budget이 충분하지 않을때에는 Hybrid > ViT. 그러나 모델이 커지면 차이는 없어짐
- convolutional local feature processing이 ViT를 도와줄거라는 일반적인 예상과 반대
-
ViT는 실험에서 사용된 범위 내에서는 scaling에 따라 saturate가 되지 않았음. → 더 model size를 키우면 성능이 개선될 여지
Inspecting Vision Transformer
- ViT가 어떻게 이미지를 분석하는지 이해하기 위해, internal representation을 분석
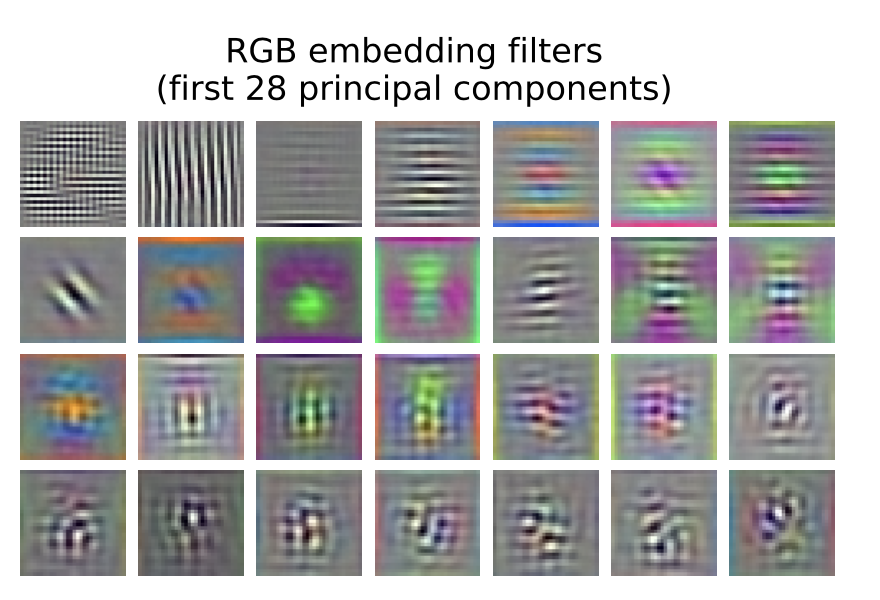
ViT의 첫 번째 layer는 flattened patch를 low-dimensional space로 projection
- 그림은 learned embedding fiter의 시각화

Projection 후에는 learned positional embedding이 patch representation에 더해지게 되는데, 이는 image 내 patch의 위치를 자동으로 학습
- 서로 가까운 patch들이 비슷한 positional embedding, 같은 row/column에 있는 패치들끼리도 유사성을 나타냄
- larger grid에서는 sinusoidal structure가 나타남
- 이렇게 2D structure를 자동으로 학습하기 때문에, 2D-aware embedding은 효과가 없음
self-attention은 ViT가 가장 낮은 layer에서부터 모든 정보를 통합적으로 사용하도록 함
- image space 상에서 image의 얼마나 멀리 떨어진 정보를 같이 사용하는지 average distance를 계산 (attention distance) → CNN의 receptive field size와 유사한 역할
- attention head 중 일부가 이미지 전체적인 정보를 사용하고, 일부는 highly localized → convolutional layer와 비슷한 역할
- classification과 semantically relevant한 영역들에 attention
Self-Supervision
트레이닝에 필요한 데이터가 너무 많기 때문에, 일일이 라벨링을 하기 힘들 수 있음 → BERT와 같이 masked patch prediction을 통해 pre-training하는 방법
- supervised pretraining에 비해서는 4% 낮은 정확도
Conclusion
Transformer의 image recognition으로의 응용 방법을 살펴봄
CV에서 self-attention을 도입한 선행연구와 달리, patch extraction을 제외하면 inductive bias 없이 학습. NLP의 Transformer에서 변형을 최소화
- large dataset에서의 pretraining을 통해 SOTA를 상회하는 결과. pretraining 또한 상대적으로 낮은 비용으로 가능
향후 연구 과제
- detection, segmentation에 적용?
- self-supervised pretraining method들에 대한 연구가 더 필요함. superised pretraining과는 성능 차이가 컸기 때문
- ViT의 크기(scale)를 더 크게 하면 performance가 더 높아질 것으로 보임